Systems
Characterizing and targeting cell functions at the origins of cell signaling.
“… abnormal cellular behavior may have its roots in bioenergetics and has nurtured the hopes that metabolic differences between cells offer new targets for low-toxicity therapeutic interventions. Warburg’s discovery (cancer metabolism) has equally encouraged the idea that metabolic intermediates may have diagnostic value, and the almost universal trait of malignant cells massively upregulating glycolysis (altered metabolism) is exploited in positron emission tomography imaging (PET).”
“Over the last 90 years, it has become obvious that metabolic switches enable cells to adapt to their bioenergetic and biosynthetic needs, respond to changing requirements for survival, expansion and longevity, and match nutrient availability and functional necessities. Not surprisingly, the need for bioenergetic plasticity is highly relevant for immune cells, which have to abruptly convert from the resting state into battle mode. Bioenergetics are particularly important in autoimmune diseases that are associated with chronic, decade-long immune activation.”
T-cell metabolism in autoimmune disease, Z Yang, E L, Matteson, J J Goronzy, C M Weyand, 2015
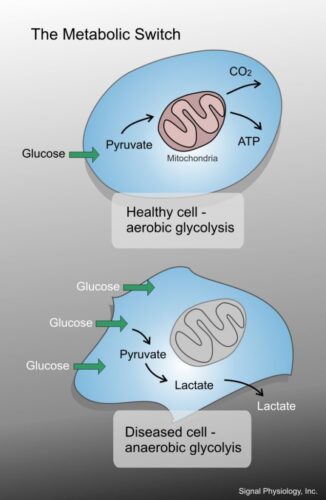
“Rather than being participators in these processes, as are genes and proteins, the metabolites produced are (diagnostic) sentinels of “what is happening” in normal physiology or pathophysiology…”
“New Opportunities from the Cancer Metabolome,”
O Aboud, R Weiss, 2013
Disease begins at the cell level, when cells experience any form of “stress,” from low-level, persistent stress to catastrophic injury. Cell stress results in an interruption to a normal cell function or physiology. In disease, the interruption is enhanced and cells are damaged. In chronic disease, the injury is persistant, variable, durable. Cell injury is more frequent. The body’s normal response to injury fails, resulting in a loss of control of the cell environment. Chronic disease, at the cell level, is characterized by an enhancement of cell signaling that the cell has been damaged or injured, damage is self-generated. In normal physiology, the cell must either be repaired or eliminated. In chronic disease, there is confusion, conflicting signals. The process is perpetual, self-driven, and escalates over time to evolve into a more dangerous disease, more destructive, more difficult to eliminate. This process is the same regardless of disease, as a wound or infection, whether the chronic condition is short- or long-term.
“Early detection” is never early…
“Disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) are detected early in the disease process in prostate cancer (PCa) patients and can persist after radical prostatectomy.”
The biology and clinical implications of prostate cancer dormancy and metastasis
Morrissey C, et al., Department of Urology, University of Washington, J Mol Med, 2016
Medicine has previously and continues to define disease by its manifestations: location in the body or of symptoms generated by the disease itself or by the body’ response to the disease. We now know that these manifestations, consequences of the disease, are very late occurrances in the disease process, a process that has developed over an extended time or years. Our ability to recognize, diagnose and determine a prognosis, must be improved. New protocols must be established.
Recent research has provided the understanding and the means, by introduction of new measurement devices and methods, to diagnose disease much earlier, at a much great level of precision. We are developing a multi-tiered, hierarchy of cell-based physiology, a “systems” approach to disease. This approach, based upon cell function (physiology) over “cell signaling,” is critical to understanding the genesis, progression and dynamics of disease. Utilizing highly bioactive nutritional agents, our understanding of disease processes, disease kinetics, allows us to monitor the disease state in real-time. To provide precise measurement of disease condition and effectiveness of nutritional agents.
